| CS-534: Packet Switch Architecture
Spring 2004 |
Department of Computer Science
© copyright: University of Crete, Greece |
1.2 Clock Domains and Elastic Buffers
|
[Up - Table of Contents] [Prev - 1.1 Rate and Throughput] |
[1.3 Mux, Output Contention - Next] |
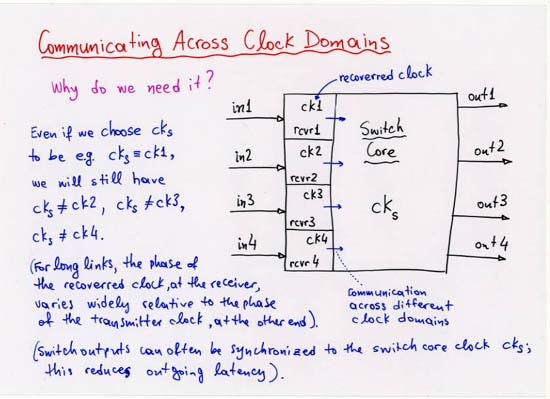
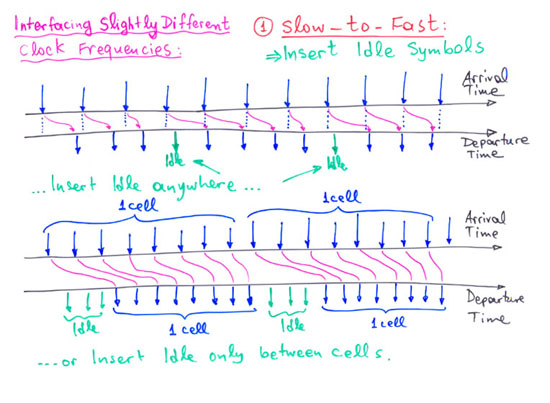
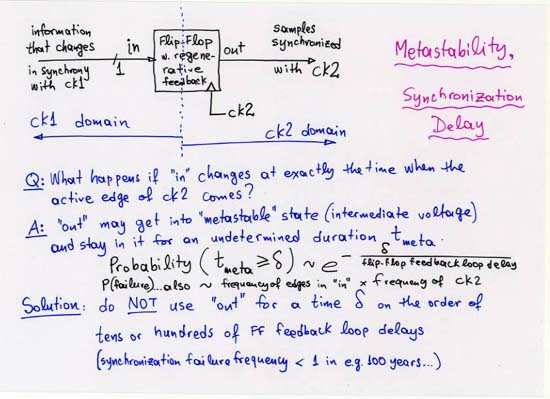
1.2.0 Multiple Clock Domains: Metastability and Synchronization
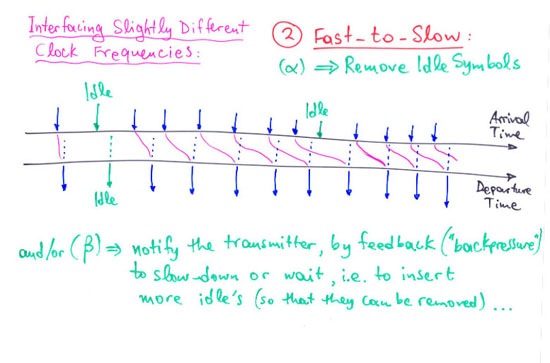
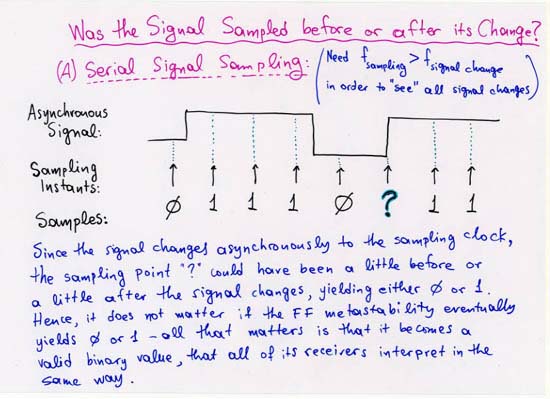
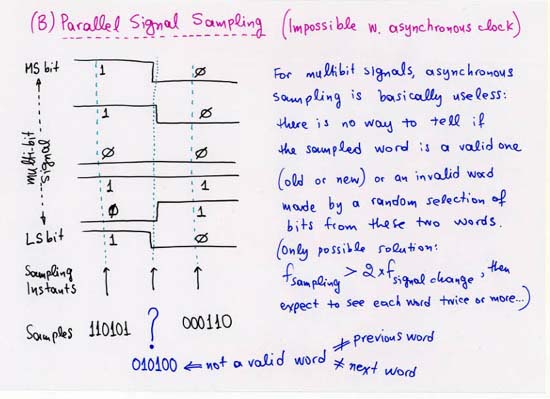
1.2.1 Serial Signals across Clock Domains: Sampling Time
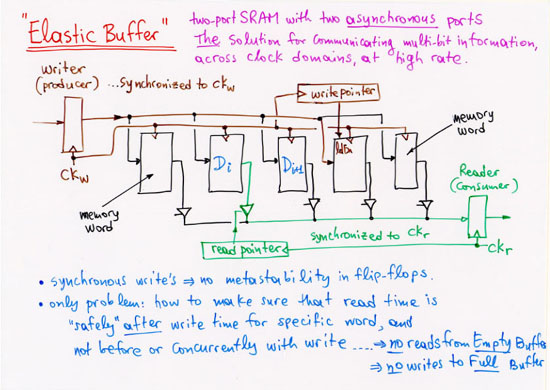
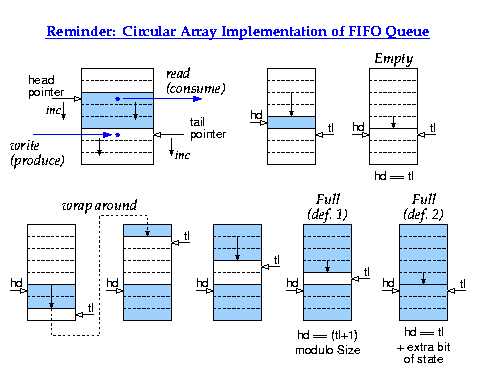
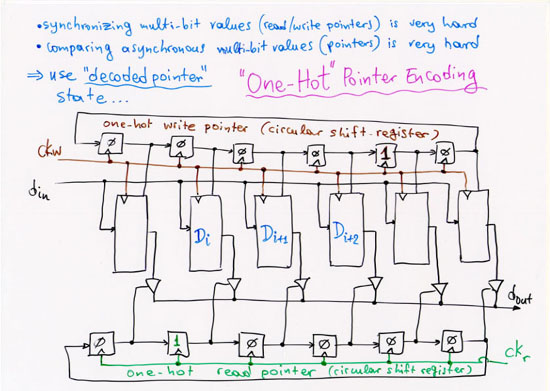
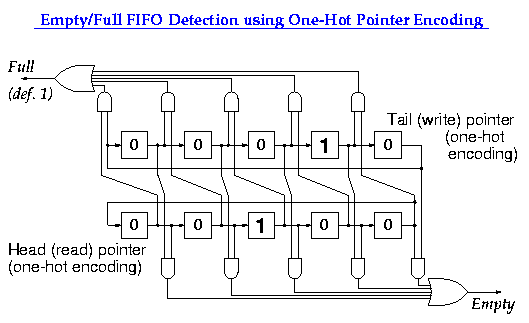
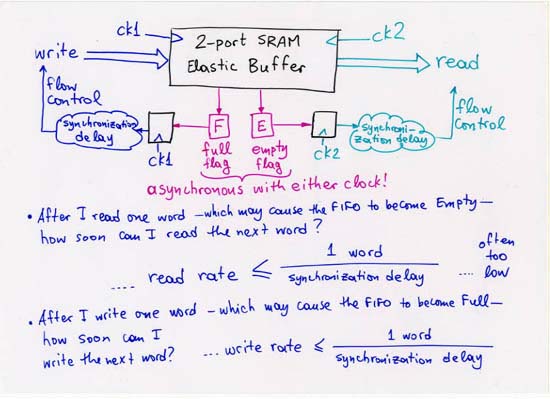
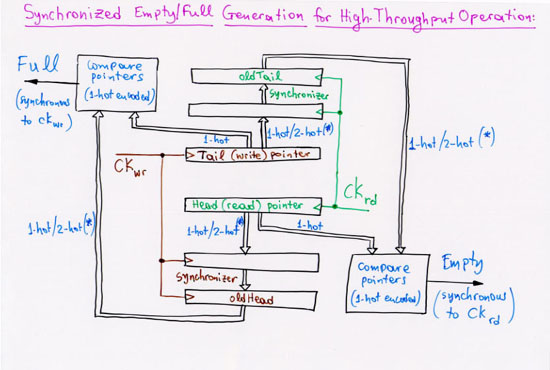
1.2.2 Parallel Signals across Clock Domains: Elastic Buffers

|
[Up - Table of Contents] [Prev - 1.1 Rate and Throughput] |
[1.3 Mux, Output Contention - Next] |
| Up to the Home Page of CS-534
|
© copyright
University of Crete, Greece.
Last updated: 18 Mar. 2004, by M. Katevenis. |