| CS-534: Packet Switch Architecture
Fall 2001 |
Department of Computer Science
© copyright: University of Crete, Greece |


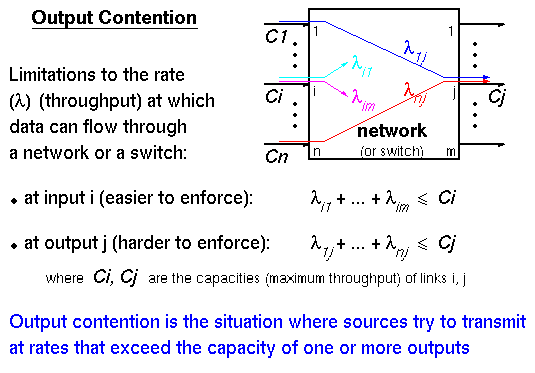
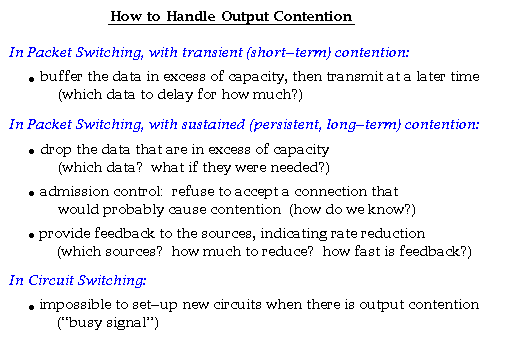
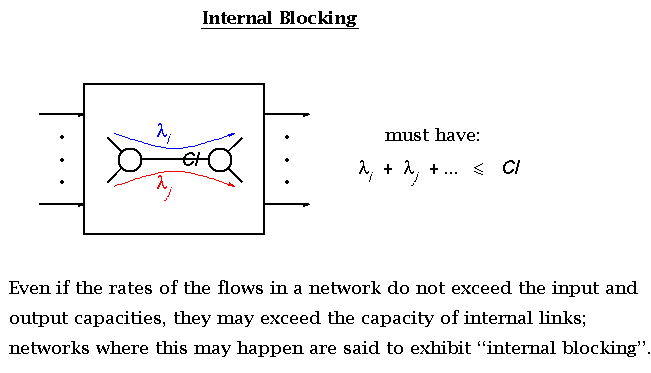
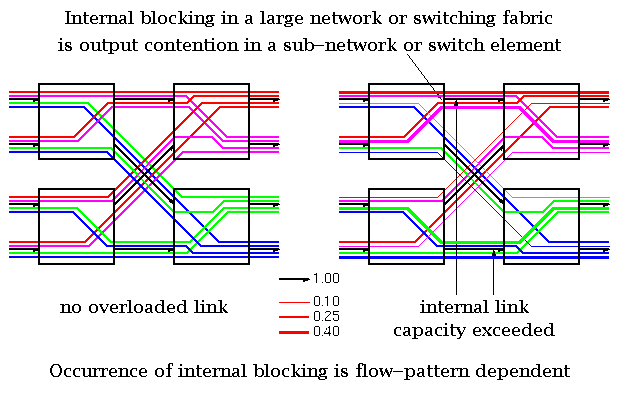
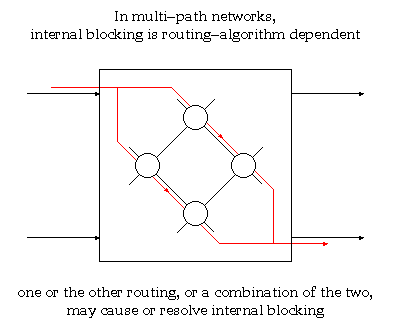
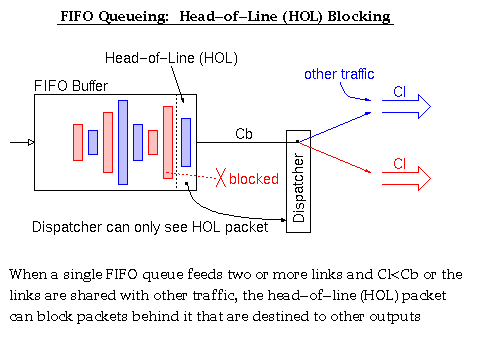
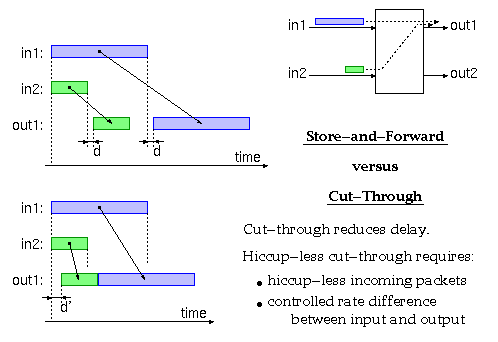
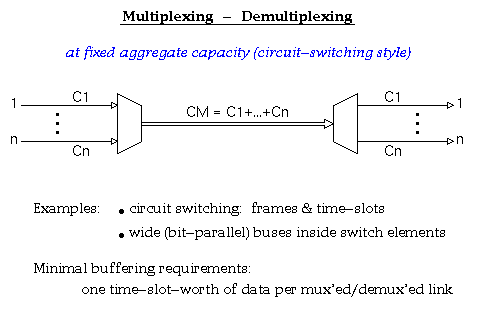
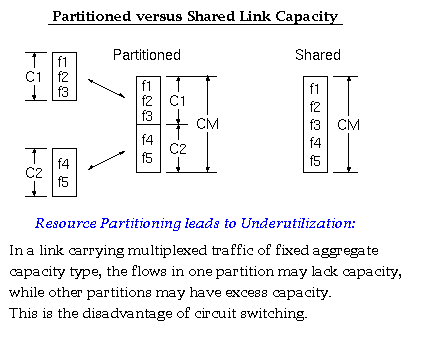
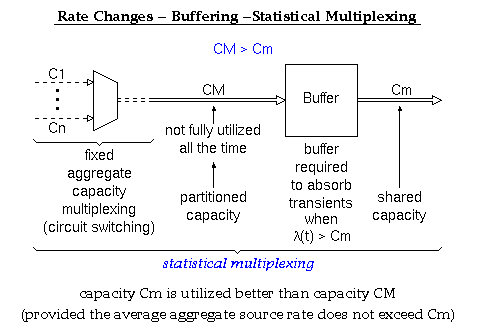
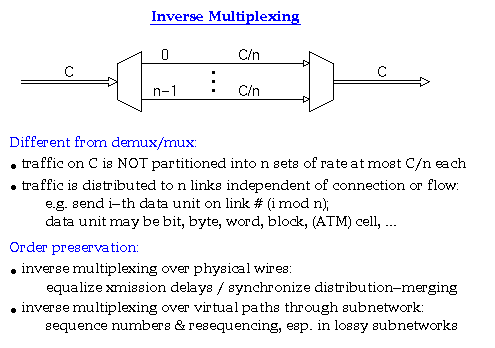
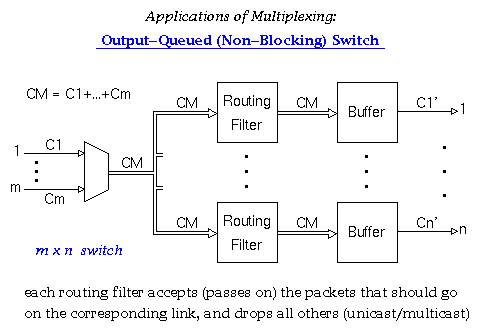
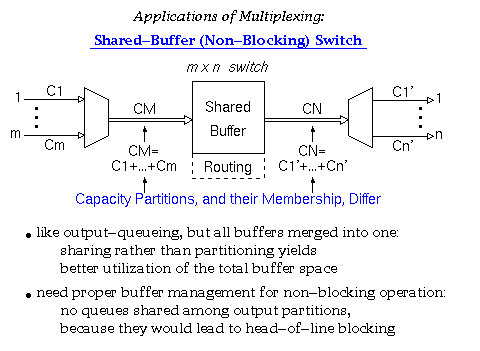
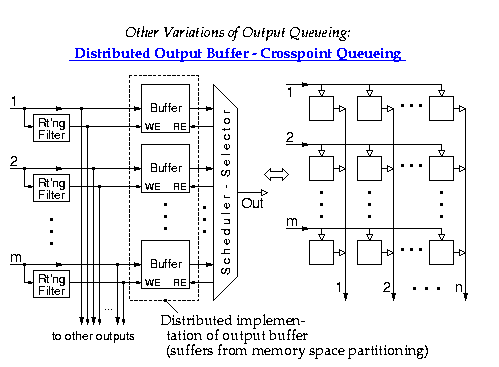

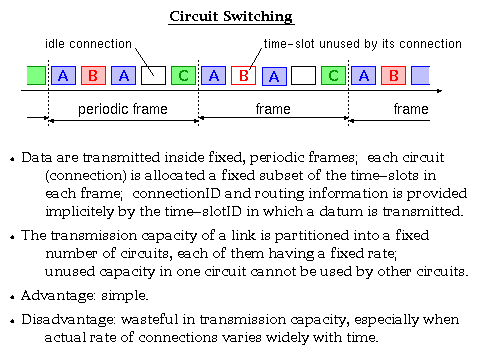
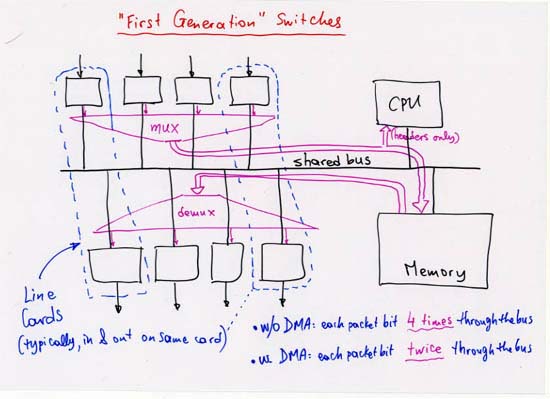
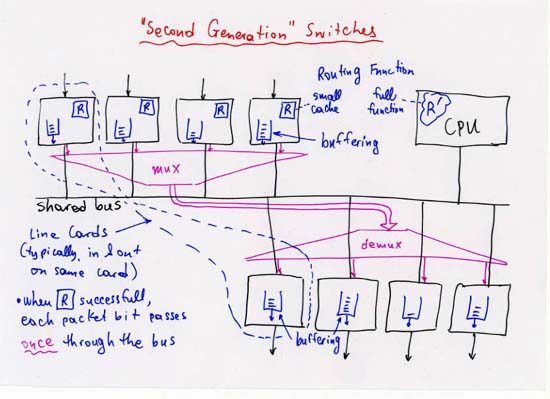
According to Keshav's book, chapter 8, the packet switch architectures can be categorized in three generations:

| Up to the Home Page of CS-534 |
© 2001 copyright: University of Crete, Greece.
Last updated: 16 Oct. 2001, by M. Katevenis. |